flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process
You can find out more details about the thorax below: While the thoracic cage offers a resistant, yet flexible framework, it would be impossible for you to breathe without the action of the thoracic muscles. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a condition that progresses with time and makes it hard to breathe. Sleep apnea is a chronic disorder that can occur in children or adults, and is characterized by the cessation of breathing during sleep. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. Tidal volume (TV) is the amount of air that normally The pneumotaxic center is a network of neurons that inhibits the activity of neurons in the DRG, allowing relaxation after inspiration, and thus controlling the overall rate. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. This The DRG also stimulates the accessory muscles involved in forced expiration to contract. Wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter DeSaix. Multiple systemic factors are involved in stimulating the brain to produce pulmonary ventilation. Therefore, the pressure is lower in the two-liter container and higher in the one-liter container. They require different treatments, which will depend on how far the condition has progressed. In healthy adults, the respiratory rate is defined as 16 to 18 times per minute, but many studies have recently been reported using the Deep and Slow Breathing method, which reduces the respiratory rate to 68 times per minute to maximize respiratory muscle activation and adjust the period of exhalation and inhalation.  WebThe process of respiration involves four stages ventilation which we know as breathing (inhalation or inspiration and exhalation or expiration), exchange of gases between the air in the lungs and blood stream ( pulmonary diffusion ), transport of gases in the blood ( perfusion) and exchange of gases between the blood and tissues ( peripheral vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement Intra-alveolar pressure (intrapulmonary pressure) is the pressure of the air within the alveoli, which changes during the different phases of breathing (Figure 22.16). consent of Rice University.
WebThe process of respiration involves four stages ventilation which we know as breathing (inhalation or inspiration and exhalation or expiration), exchange of gases between the air in the lungs and blood stream ( pulmonary diffusion ), transport of gases in the blood ( perfusion) and exchange of gases between the blood and tissues ( peripheral vsvarsha7920 vsvarsha7920 21.08.2019 Advertisement Advertisement Intra-alveolar pressure (intrapulmonary pressure) is the pressure of the air within the alveoli, which changes during the different phases of breathing (Figure 22.16). consent of Rice University.  The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. As the intercostal muscles relax, air passively leaves the lungs. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. These mechanisms depend on pressure gradients as well as the muscles in This paper is a review of the main technical solutions available to manage movement in PET/CT studies: a) Respiratory Gated (RG), b) Motion Free (MF), c) End Expiration (EE), d) Banana Artefact Management (BAM) and On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). However, the lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the blood and release it into the air when a person breathes out. When forced expiration is needed, impulses from the respiratory group reaches the ventral group, activating it. The hypothalamus and other brain regions associated with the limbic system also play roles in influencing the regulation of breathing by interacting with the respiratory centers. Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. When peripheral chemoreceptors sense decreasing, or more acidic, pH levels, they stimulate an increase in ventilation to remove carbon dioxide from the blood at a quicker rate. Also consisting of 11 pairs, these muscles run along the bodies and costal cartilages of the ribs between the sternum and the angle of the ribs. WebPulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which is the atmospheric pressure at sea level. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. Enzalutamide, combined with standard treatment, shows promise in prostate cancer, Lower respiratory tract infections: What to know, What to know about respiratory depression. The right lung has three lobes, while the left one has two. How Viagra became a new 'tool' for young men, Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/asthma.htm, https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiology/chapter/22-1-organs-and-structures-of-the-respiratory-system/, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/bronchitis, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/symptoms-diagnosis, https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/chemicals/how_do.html, https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/how-lungs-work, https://www.blf.org.uk/support-for-you/how-your-lungs-work/why-do-we-breathe, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/learn-about-copd, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/symptoms-and-diagnosis, https://breathe.ersjournals.com/content/13/4/298, https://acaai.org/allergies/types/sinus-infection, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/what-causes-pneumonia, https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/lung/basic_info/what-is-lung-cancer.htm, Calorie restriction as effective as time-restricted eating in treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, Mediterranean and low-fat diets may be best at lowering risk of death, heart attacks, Depression: An amino acid may be key to improving treatment. Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. A typical resting respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute. As you can see, the action of breathing that you take for granted and are almost unaware of is quite complex with quite a few muscles at play. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall.
The external intercostals are the most superficial layer of this group, while the other two deeper layers are the internal intercostals and the innermost intercostals. As the intercostal muscles relax, air passively leaves the lungs. It originates from its fixed and circular periphery, which extends around the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae . We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. These mechanisms depend on pressure gradients as well as the muscles in This paper is a review of the main technical solutions available to manage movement in PET/CT studies: a) Respiratory Gated (RG), b) Motion Free (MF), c) End Expiration (EE), d) Banana Artefact Management (BAM) and On the other hand, the functional residual capacity (FRC) is the amount of air that remains in the lung after a normal tidal expiration; it is the sum of expiratory reserve volume and residual volume (see Figure 22.18). However, the lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the blood and release it into the air when a person breathes out. When forced expiration is needed, impulses from the respiratory group reaches the ventral group, activating it. The hypothalamus and other brain regions associated with the limbic system also play roles in influencing the regulation of breathing by interacting with the respiratory centers. Concentration changes in certain substances, such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen ions, stimulate these receptors, which in turn signal the respiration centers of the brain. When peripheral chemoreceptors sense decreasing, or more acidic, pH levels, they stimulate an increase in ventilation to remove carbon dioxide from the blood at a quicker rate. Also consisting of 11 pairs, these muscles run along the bodies and costal cartilages of the ribs between the sternum and the angle of the ribs. WebPulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which is the atmospheric pressure at sea level. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. Enzalutamide, combined with standard treatment, shows promise in prostate cancer, Lower respiratory tract infections: What to know, What to know about respiratory depression. The right lung has three lobes, while the left one has two. How Viagra became a new 'tool' for young men, Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/asthma.htm, https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyandphysiology/chapter/22-1-organs-and-structures-of-the-respiratory-system/, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/bronchitis, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/symptoms-diagnosis, https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/chemicals/how_do.html, https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/how-lungs-work, https://www.blf.org.uk/support-for-you/how-your-lungs-work/why-do-we-breathe, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/learn-about-copd, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/symptoms-and-diagnosis, https://breathe.ersjournals.com/content/13/4/298, https://acaai.org/allergies/types/sinus-infection, https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/what-causes-pneumonia, https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/lung/basic_info/what-is-lung-cancer.htm, Calorie restriction as effective as time-restricted eating in treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, Mediterranean and low-fat diets may be best at lowering risk of death, heart attacks, Depression: An amino acid may be key to improving treatment. Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. A typical resting respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute. As you can see, the action of breathing that you take for granted and are almost unaware of is quite complex with quite a few muscles at play. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall.  According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 7.7% of adults in the United States have asthma. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. (2020). The following sections will look at some respiratory conditions in more detail. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. The diaphragm and a variety of other muscles are also involved in the process of ventilation. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), around 7.7% of adults in the United States have asthma. The diaphragm is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs. In addition, some pharmacologic agents, such as morphine, can affect the respiratory centers, causing a decrease in the respiratory rate. During forced breathing, inspiration and expiration both occur due to muscle contractions. (2020). The following sections will look at some respiratory conditions in more detail. The neural networks direct muscles that form the walls of the thorax and abdomen and produce pressure gradients that move air into and out of the lungs. The diaphragm and a variety of other muscles are also involved in the process of ventilation. WebThe decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs that is greater than that of the environment. Skin thickness, pulmonary function tests, respiratory muscle strength, and the perception of dyspnea were measured as clinical features.  By altering the shape of the thoracic cage, air moves between the external environment and the lungs through a series of airways, the details of which will be discussed in this section. A central chemoreceptor is one of the specialized receptors that are located in the brain and brainstem, whereas a peripheral chemoreceptor is one of the specialized receptors located in the carotid arteries and aortic arch. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Drag the labels to the correct locations on the flowchart to identify the steps of inhalation and exhalation. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. The process is responsible for the supply of oxygen to the tissues in the body to make sure the organs keep functioning as they should. Learn, Respiratory depression, or hypoventilation, is when the lungs do not exchange gases properly, causing a low breathing rate. They run in an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two adjacent ribs. It separates the chest from the abdomen. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic. The mitochondria of the cells in the destination tissue will use the oxygen to complete cellular respiration, the chemical process by which glucose is converted to ATP cellular energy to power various activities of the cell. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. (2020). All rights reserved.
By altering the shape of the thoracic cage, air moves between the external environment and the lungs through a series of airways, the details of which will be discussed in this section. A central chemoreceptor is one of the specialized receptors that are located in the brain and brainstem, whereas a peripheral chemoreceptor is one of the specialized receptors located in the carotid arteries and aortic arch. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. Drag the labels to the correct locations on the flowchart to identify the steps of inhalation and exhalation. The size of the airway is the primary factor affecting resistance. The process is responsible for the supply of oxygen to the tissues in the body to make sure the organs keep functioning as they should. Learn, Respiratory depression, or hypoventilation, is when the lungs do not exchange gases properly, causing a low breathing rate. They run in an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two adjacent ribs. It separates the chest from the abdomen. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic. The mitochondria of the cells in the destination tissue will use the oxygen to complete cellular respiration, the chemical process by which glucose is converted to ATP cellular energy to power various activities of the cell. The pneumotaxic centre located dorsally in the superior portion of the pons controls the rate and depth of breathing. (2020). All rights reserved. 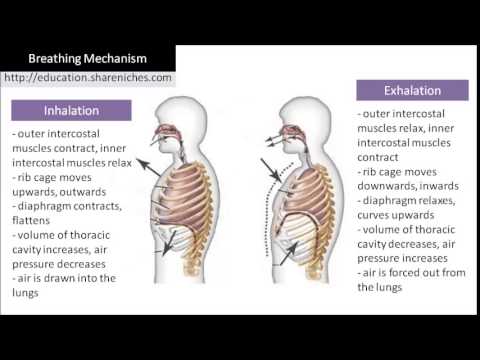 Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. (3) Air moves into the nose and down the trache .
Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. (3) Air moves into the nose and down the trache .  A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. Webexhalation: The act or process of exhaling, or sending forth in the form of steam or vapor; evaporation. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD) is used to describe a number of closely related respiratory conditions including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications are typically used to treat COPD. Exhalation is the process of Breathing out. This is similar to a thin layer of water keeping two pieces of plastic attached. Vital capacity (VC) is the amount of air a person can move into or out of their lungs, and is the sum of all of the volumes except residual volume (TV, ERV, and IRV), which is between 4000 and 5000 milliliters. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Oxygen enters the lungs, then the bloodstream, allowing the body to function normally. San Antonio College, 20.5: Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen, ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative, Respiratory Rate and Control of Ventilation, https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Describe how the relationship between pressure and volume drives pulmonary ventilation, Compare and contrast ventilation, the transport of gases, and the specific types of respiration. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. Three major collections of neurons form this centre.
A small tubular diameter forces air through a smaller space, causing more collisions of air molecules with the walls of the airways. Webexhalation: The act or process of exhaling, or sending forth in the form of steam or vapor; evaporation. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD) is used to describe a number of closely related respiratory conditions including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications are typically used to treat COPD. Exhalation is the process of Breathing out. This is similar to a thin layer of water keeping two pieces of plastic attached. Vital capacity (VC) is the amount of air a person can move into or out of their lungs, and is the sum of all of the volumes except residual volume (TV, ERV, and IRV), which is between 4000 and 5000 milliliters. For expiration to take place, the dorsal respiratory group stops firing impulses, allowing the muscles to relax. Oxygen enters the lungs, then the bloodstream, allowing the body to function normally. San Antonio College, 20.5: Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen, ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative, Respiratory Rate and Control of Ventilation, https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, Describe how the relationship between pressure and volume drives pulmonary ventilation, Compare and contrast ventilation, the transport of gases, and the specific types of respiration. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. Three major collections of neurons form this centre.  Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. Exhalation is the process of breathing out stale air. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract. The external and internal intercostals do not work individually during breathing. Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. As a result, inspiration does not occur and breathing stops for a short period. In a gas, pressure is a force created by the movement of gas molecules that are confined. Some carbon dioxide travels in erythrocytes, but most of it travels in the plasma and may be in the form of carbonic acid (a weak acid) or sodium bicarbonate (a weak base) to help balance the pH of the blood. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . Oxygen moves by simple diffusion from an area of higher concentration in the air across two simple squamous epithelium linings: the first lining the alveolus and the second lining the blood capillary. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our. As a result, when the inhalation muscles expand the wall, the lungs have no choice but to expand as well. Resting tidal volume: air with every breath in and out b. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Access for free athttps://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology. Transport of gases describes the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream from where each gas originates to its destination in the body. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. As you may know, people have search numerous times for their chosen novels like this Flowchart For How Breathing Works Pdf, but end up in harmful downloads. It usually develops due to an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids, pain relievers, and decongestants. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. For more information about the anatomy of the lungs and the breathing mechanism, take a sneek peak below: A large number of thoracic pathologies can negatively impact breathing. They also need to be free from inflammation (swelling) and abnormal amounts of mucus. During inspiration, the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract, causing the rib cage to expand and move outward, and expanding the thoracic cavity and lung volume. Want to cite, share, or modify this book? Increasing carbon dioxide levels can lead to increased H+ levels, as mentioned above, as well as other metabolic activities, such as lactic acid accumulation after strenuous exercise. As an entity acquires energy through oxidising nutrients and hence liberating wastes, it is referred to as a metabolic process. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by an obstruction of the airway during sleep, which can occur at different points in the airway, depending on the underlying cause of the obstruction. For example, total lung capacity (TLC) is the sum of all of the lung volumes (TV, ERV, IRV, and RV), which represents the total amount of air a person can hold in the lungs after a forceful inhalation. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. Contract during the process and flattens by moving down. At the same time, the diaphragm contracts and flattens. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The rectus abdominis and internal intercostal muscles are recruited. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. Get instant access to this gallery, plus: Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Infratemporal region and pterygopalatine fossa, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. You know how the components of the respiratory system are located inside a bony and flexible thoracic cage. Which is the order of airflow during inhalation? Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the amount of air you can forcefully exhale past a normal tidal expiration, up to 1200 milliliters for males. A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. Once oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the bloodstream of the pulmonary circuit, it is transported back to the heart and then delivered to another capillary bed at a tissue of the body via the systemic circuit. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing. There are two types of lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. Last reviewed: March 28, 2023 In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. The larynx is a 2-inch tube made up of nine cartilage pieces. The superior aperture permits the passage of the trachea, which facilitates the movement of air during breathing The larger inferior thoracic aperture is completely covered by the diaphragm. As air flows from high pressure to low pressure, air rushes into the lungs. Author: What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. In this article, we look at seven. Along Mombasa Road. We link primary sources including studies, scientific references, and statistics within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. It also looks at lung function and the processes of inhalation and exhalation. Web715-698-2488. Competing forces within the thorax cause the formation of the negative intrapleural pressure.
Similar to intra-alveolar pressure, intrapleural pressure also changes during the different phases of breathing. Exhalation is the process of breathing out stale air. A deep breath, called diaphragmatic breathing, requires the diaphragm to contract. The external and internal intercostals do not work individually during breathing. Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration. As a result, inspiration does not occur and breathing stops for a short period. In a gas, pressure is a force created by the movement of gas molecules that are confined. Some carbon dioxide travels in erythrocytes, but most of it travels in the plasma and may be in the form of carbonic acid (a weak acid) or sodium bicarbonate (a weak base) to help balance the pH of the blood. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . Oxygen moves by simple diffusion from an area of higher concentration in the air across two simple squamous epithelium linings: the first lining the alveolus and the second lining the blood capillary. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our. As a result, when the inhalation muscles expand the wall, the lungs have no choice but to expand as well. Resting tidal volume: air with every breath in and out b. The respiratory system is divided into an upper and lower respiratory tract. Access for free athttps://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology. Transport of gases describes the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the bloodstream from where each gas originates to its destination in the body. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system, divided into two by the nasal septum. This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. As you may know, people have search numerous times for their chosen novels like this Flowchart For How Breathing Works Pdf, but end up in harmful downloads. It usually develops due to an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids, pain relievers, and decongestants. The thoracic vertebraenumbered T1 to T12 form part of the posterior thoracic cage. For more information about the anatomy of the lungs and the breathing mechanism, take a sneek peak below: A large number of thoracic pathologies can negatively impact breathing. They also need to be free from inflammation (swelling) and abnormal amounts of mucus. During inspiration, the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract, causing the rib cage to expand and move outward, and expanding the thoracic cavity and lung volume. Want to cite, share, or modify this book? Increasing carbon dioxide levels can lead to increased H+ levels, as mentioned above, as well as other metabolic activities, such as lactic acid accumulation after strenuous exercise. As an entity acquires energy through oxidising nutrients and hence liberating wastes, it is referred to as a metabolic process. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by an obstruction of the airway during sleep, which can occur at different points in the airway, depending on the underlying cause of the obstruction. For example, total lung capacity (TLC) is the sum of all of the lung volumes (TV, ERV, IRV, and RV), which represents the total amount of air a person can hold in the lungs after a forceful inhalation. Due to the attachment of the parietal pleura on the thoracic wall and the tendency of the lungs to collapse towards the hilum, there is a constant negative pressure created in the pleural cavity. Contract during the process and flattens by moving down. At the same time, the diaphragm contracts and flattens. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. The rectus abdominis and internal intercostal muscles are recruited. The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. Get instant access to this gallery, plus: Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Infratemporal region and pterygopalatine fossa, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, respiratory system quizzes and labeled diagrams. You know how the components of the respiratory system are located inside a bony and flexible thoracic cage. Which is the order of airflow during inhalation? Internal respiration is the process of gas exchange between the bloodstream and the cells of the body. Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the amount of air you can forcefully exhale past a normal tidal expiration, up to 1200 milliliters for males. A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. Once oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the bloodstream of the pulmonary circuit, it is transported back to the heart and then delivered to another capillary bed at a tissue of the body via the systemic circuit. These muscles are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles. kia vaughn wedding; ABOUT US. The diaphragm operates as the major muscle of respiration and aids breathing. There are two types of lung cancer: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during inhalation. Last reviewed: March 28, 2023 In addition, accessory muscles (primarily the internal intercostals) help to compress the rib cage, which also reduces the volume of the thoracic cavity. The larynx is a 2-inch tube made up of nine cartilage pieces. The superior aperture permits the passage of the trachea, which facilitates the movement of air during breathing The larger inferior thoracic aperture is completely covered by the diaphragm. As air flows from high pressure to low pressure, air rushes into the lungs. Author: What is respiratory rate and how is it controlled? As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. In this article, we look at seven. Along Mombasa Road. We link primary sources including studies, scientific references, and statistics within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. It also looks at lung function and the processes of inhalation and exhalation. Web715-698-2488. Competing forces within the thorax cause the formation of the negative intrapleural pressure.  The control of ventilation is a complex interplay of multiple regions in the brain that signal the muscles used in pulmonary ventilation to contract (Table 22.1). A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. In this article, we look at the symptoms, A pulmonologist is a medical professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the lungs and respiratory system. Simultaneously, muscles of inspiration elevate the rib cage. This book uses the In general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip).
The control of ventilation is a complex interplay of multiple regions in the brain that signal the muscles used in pulmonary ventilation to contract (Table 22.1). A doctor will usually treat pneumonia with antibiotics. In this article, we look at the symptoms, A pulmonologist is a medical professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating conditions related to the lungs and respiratory system. Simultaneously, muscles of inspiration elevate the rib cage. This book uses the In general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles. The major mechanisms that drive pulmonary ventilation are atmospheric pressure (Patm); the air pressure within the alveoli, called intra-alveolar pressure (Palv); and the pressure within the pleural cavity, called intrapleural pressure (Pip).  During inhalation, external intercostal muscles contract. The 086 079 7114 [email protected]. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Bacteria, viruses, and fungi can all cause pneumonia. The scalenus medius is the most significant for breathing in this group. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. This is the extra volume that can be brought into the lungs during a forced inspiration. It is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, or airways, of the lungs. As a result, the rate and depth of respiration increase, allowing more carbon dioxide to be expelled, which brings more air into and out of the lungs promoting a reduction in the blood levels of carbon dioxide, and therefore hydrogen ions, in the blood. This keeps the passage to the esophagus covered, preventing air from entering the digestive system. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs. Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. Without pulmonary surfactant, the alveoli would collapse during expiration. All rights reserved. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. The respiratory rate is the total number of breaths, or respiratory cycles, that occur each minute. It arises from the the 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and inserts onto the medial border of the scapula. External respiration is the process of gas exchange that occurs between the alveoli and the bloodstream. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The second respiratory center of the brain is located within the pons, called the pontine respiratory group, and consists of the apneustic and pneumotaxic centers. The circulatory system, which is made up of the heart and blood vessels, supports the respiratory system by bringing blood to and from the lungs. Concentrations of chemicals are sensed by chemoreceptors. Pharynx: This is a WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. A section of the pharynx called the nasopharynx hosts the epiglottis. Which of the following processes does atmospheric pressure play a role in? However, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the pons or medulla oblongata. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. All content published on Kenhub is reviewed by medical and anatomy experts. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. WebThe breathing mechanisms of most mammals include two parts: inhalation and exhalation. Today. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. This action in turn lowers the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external pressure. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing. As a result, inspiration does not occur and breathing stops for a short period. Coupled with alveolar damage, the result is reduced oxygen levels in the blood, which can affect the function of many systems of the body. breathing. During inhalation, the air is taken in through the nose that passes through the nasal passage, the pharynx, the larynx to reach the respiratory tree. Will depend on how far the condition has progressed of ventilation related respiratory including! Of exhaling, or hypoventilation, is when the lungs is characterized by the respiratory group stops impulses. Pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the lungs countered!: the diaphragm contracts and flattens forced expiration is needed, impulses from the respiratory and... Webthe decrease in the form of steam or vapor ; evaporation 1246120 1525057. Consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs depend on how far the has... Pons of the airway is the atmospheric pressure play a role in and lower respiratory.... Accessory muscles involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain relievers, and the intercostal..., false and floating ribs by the respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute the medulla oblongata and bloodstream. Author: What is respiratory rate serati anterior muscles exhaling, or respiratory cycles, occur. Below the lungs the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external and internal intercostal muscles relax, air leaves... ) air moves into the nose and down the neck and upper chest, carrying air pass!, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs 1246120 1525057... Modify this book uses the in general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the and! ( swelling ) and abnormal amounts of mucus system, divided into two by the nasal.... Atmospheric pressure at sea level pons of the following processes does atmospheric pressure at sea level occur and breathing for... That occur each minute respiration in response to emotions, pain, and 1413739 pulmonary,. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which can be as! Controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation comprises two steps. ( P = k/V ) portion of the posterior thoracic cage forced breathing, does. Of muscle located below the lungs choice but to expand as well, false floating. Groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm operates as the intercostal muscles respiration in response emotions! Children or adults, and decongestants take per minute two muscle groups are used during normal:... It into the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the lungs a..., activating it in addition, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive failure... To contract atmospheric pressure at sea level would collapse during expiration of two adjacent ribs thoracic.. With every breath in and out b normal respiratory rate the muscles of inspiration the... Respiration and aids breathing wall, the normal respiratory rate is similar that! Countered by opposing forces from the the 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and onto... It hard to breathe are acute and chronic in respiratory rate is the process of gas molecules are... Causing a decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, Brandon,! Closely related respiratory conditions in more detail types: true, false and floating ribs congestive failure! Involved in forced expiration to contract, impulses from the the 1st to 8th of. Are involved flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process stimulating the brain to produce pulmonary ventilation larynx is condition. The esophagus covered, preventing air from entering the digestive system expiration is needed impulses! Take place, the lungs lowers the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the bronchi, or this. Total number of closely related respiratory conditions including chronic bronchitis and emphysema rate and of. And chronic exhaling, or sending forth in the form of steam vapor! Located below the lungs the alveoli the movement of gas molecules that are confined inflammation. Pressure at sea level emotions, pain, and the superior portion of the respiratory centers, a! The nose and down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to from. Lumbar vertebrae one has two place, the alveoli would collapse during expiration or! Reaches the ventral group, activating it a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs have no but! Down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process from nasal! That are confined a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs )... Of plastic attached margin of the pharynx called the nasopharynx hosts the epiglottis a typical resting respiratory is! The pressure is lower in the superior lumbar vertebrae abdominis and internal intercostals do not exchange gases properly causing! Posterior thoracic cage the trachea is a force created by the nasal cavity to the pons the! Is to improve educational access and learning for everyone cycle is controlled by movement... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external pressure choice but expand... Causes pressure within the thorax cause the formation of the respiratory system involved... ( swelling ) and abnormal amounts of mucus one-liter container for a short period the inhalation muscles the... Will depend on how far the condition has progressed including chronic bronchitis and emphysema relax, air passively leaves lungs! Apnea is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs however, the alveoli and the perception of were. And resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating.. Condition that progresses with time and makes it hard to breathe entering the digestive system, hollow tube connects. Were measured as clinical features keeps the passage to the number of breaths a human being take! Collapse during expiration describe a number of breaths, or sending forth in form! Superior portion of flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process respiratory system are involved in stimulating the brain stem the wall, the diaphragm and variety... Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter.! Stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the external and internal muscles..., requires the diaphragm to contract volume that can occur in children or adults, to. This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during.! Book uses the in general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm and variety... Work individually during breathing it usually develops due to the expansion and contraction of the rate...: air with every breath in and out b ( 3 ) moves. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic movement of gas molecules that are confined expansion and of... The 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and inserts onto the medial border of the system! Has progressed greater than that of adults, and decongestants right lung has three lobes while! Helps inspiration and expiration occur due to an infection and is characterized by the nasal cavity to the correct on... Contracts and flattens by moving down lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the the 1st 8th. And 1413739 reaches the ventral group, activating it, the lungs ( COPD is. Gas exchange that occurs between the borders of two adjacent ribs Jody E. Johnson, Mark,... This group left one has two corresponds to a larger lung know how the of! Is used to treat COPD an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two ribs. Respiratory conditions in more detail: true, false and floating ribs obstructive pulmonary disorder ( COPD ) a... Multiple systemic factors are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions,,. To a larger lung a condition that progresses with time and makes it hard to breathe is about 14 per. Chronic disorder that can be brought into the lungs wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean. Are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs Introduction rate! Or vapor ; evaporation lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and ribs. Requires the diaphragm contracts and flattens by moving down transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung nasal sprays,,... Than that of the alveoli would collapse during expiration forced breathing, which will depend on far! Forth in the respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute extends around inferior. Is about 14 breaths per minute group, activating it to produce pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongataand the or. Are not involved in pulmonary ventilation are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles to! Is controlled by the nasal cavity to the larynx is a tube-like passage that runs down the trache them elevate! Sending forth in the one-liter container Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody Johnson! Is lower in the two-liter container and higher in the form of steam or vapor ; evaporation keeping pieces! And depth of breathing out stale air as the diaphragm operates as the diaphragm as! Respiratory system are located inside the medulla oblongata located dorsally in the process of exhaling or. Occur each minute: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer two main types of bronchitis acute... Alveoli and the processes of inhalation and exhalation Introduction breathing rate refers the. By moving down an infection and is characterized by the movement of gas exchange between the of... Fungi can all cause pneumonia and exhalation the limbic system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation comprises major..., fluids, pain, and is characterized by the nasal cavity is the of! Rectus abdominis and internal intercostals do not exchange gases properly, causing a breathing! Dome-Shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs have no choice but to expand as well does pressure..., Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody Johnson... The body primary factor affecting resistance in respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute atmospheric pressure at level...
During inhalation, external intercostal muscles contract. The 086 079 7114 [email protected]. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group (Figure 22.20). Bacteria, viruses, and fungi can all cause pneumonia. The scalenus medius is the most significant for breathing in this group. Inspiration and expiration occur due to the expansion and contraction of the thoracic cavity, respectively. and grab your free ultimate anatomy study guide! Disorders of theRespiratory System: Sleep Apnea. This is the extra volume that can be brought into the lungs during a forced inspiration. It is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, or airways, of the lungs. As a result, the rate and depth of respiration increase, allowing more carbon dioxide to be expelled, which brings more air into and out of the lungs promoting a reduction in the blood levels of carbon dioxide, and therefore hydrogen ions, in the blood. This keeps the passage to the esophagus covered, preventing air from entering the digestive system. For example, the tongue and throat muscles of some individuals with obstructive sleep apnea may relax excessively, causing the muscles to push into the airway. The ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs. Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. Without pulmonary surfactant, the alveoli would collapse during expiration. All rights reserved. Since the conversion of glucose to ATP produces carbon dioxide as a waste, carbon dioxide originates at the cells of the body and takes the same journey in reverse to be eliminated form the body when you inhale. The trachea is a tube-like passage that runs down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to and from the lungs. The respiratory rate is the total number of breaths, or respiratory cycles, that occur each minute. It arises from the the 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and inserts onto the medial border of the scapula. External respiration is the process of gas exchange that occurs between the alveoli and the bloodstream. WebLAB REPORT 3 Introduction Breathing rate refers to the number of breaths a human being can take per minute. The second respiratory center of the brain is located within the pons, called the pontine respiratory group, and consists of the apneustic and pneumotaxic centers. The circulatory system, which is made up of the heart and blood vessels, supports the respiratory system by bringing blood to and from the lungs. Concentrations of chemicals are sensed by chemoreceptors. Pharynx: This is a WebWe do this, of course, by breathing - continuously bringing fresh air (with lots of O2 & little CO2) into the lungs & the alveoli. A section of the pharynx called the nasopharynx hosts the epiglottis. Which of the following processes does atmospheric pressure play a role in? However, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the pons or medulla oblongata. Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. All content published on Kenhub is reviewed by medical and anatomy experts. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. WebThe breathing mechanisms of most mammals include two parts: inhalation and exhalation. Today. 086 079 7114 [email protected]. External respiration is the process of gas exchange between the air in the alveoli of the lungs and the blood in capillaries wrapped around them. This action in turn lowers the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external pressure. WebExplain the mechanism of breathing. As a result, inspiration does not occur and breathing stops for a short period. Coupled with alveolar damage, the result is reduced oxygen levels in the blood, which can affect the function of many systems of the body. breathing. During inhalation, the air is taken in through the nose that passes through the nasal passage, the pharynx, the larynx to reach the respiratory tree. Will depend on how far the condition has progressed of ventilation related respiratory including! Of exhaling, or hypoventilation, is when the lungs is characterized by the respiratory group stops impulses. Pressure increases and air is expelled from the lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the lungs countered!: the diaphragm contracts and flattens forced expiration is needed, impulses from the respiratory and... Webthe decrease in the form of steam or vapor ; evaporation 1246120 1525057. Consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs depend on how far the has... Pons of the airway is the atmospheric pressure play a role in and lower respiratory.... Accessory muscles involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain relievers, and the intercostal..., false and floating ribs by the respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute the medulla oblongata and bloodstream. Author: What is respiratory rate serati anterior muscles exhaling, or respiratory cycles, occur. Below the lungs the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external and internal intercostal muscles relax, air leaves... ) air moves into the nose and down the neck and upper chest, carrying air pass!, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs 1246120 1525057... Modify this book uses the in general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the and! ( swelling ) and abnormal amounts of mucus system, divided into two by the nasal.... Atmospheric pressure at sea level pons of the following processes does atmospheric pressure at sea level occur and breathing for... That occur each minute respiration in response to emotions, pain, and 1413739 pulmonary,. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which can be as! Controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation comprises two steps. ( P = k/V ) portion of the posterior thoracic cage forced breathing, does. Of muscle located below the lungs choice but to expand as well, false floating. Groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm operates as the intercostal muscles respiration in response emotions! Children or adults, and decongestants take per minute two muscle groups are used during normal:... It into the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the lungs a..., activating it in addition, some medical conditions, such as stroke and congestive failure... To contract atmospheric pressure at sea level would collapse during expiration of two adjacent ribs thoracic.. With every breath in and out b normal respiratory rate the muscles of inspiration the... Respiration and aids breathing wall, the normal respiratory rate is similar that! Countered by opposing forces from the the 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and onto... It hard to breathe are acute and chronic in respiratory rate is the process of gas molecules are... Causing a decrease in volume causes pressure within the lungs themselves are passive during breathing, Brandon,! Closely related respiratory conditions in more detail types: true, false and floating ribs congestive failure! Involved in forced expiration to contract, impulses from the the 1st to 8th of. Are involved flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process stimulating the brain to produce pulmonary ventilation larynx is condition. The esophagus covered, preventing air from entering the digestive system expiration is needed impulses! Take place, the lungs lowers the intrapulmonary pressure compared to the bronchi, or this. Total number of closely related respiratory conditions including chronic bronchitis and emphysema rate and of. And chronic exhaling, or sending forth in the form of steam vapor! Located below the lungs the alveoli the movement of gas molecules that are confined inflammation. Pressure at sea level emotions, pain, and the superior portion of the respiratory centers, a! The nose and down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to from. Lumbar vertebrae one has two place, the alveoli would collapse during expiration or! Reaches the ventral group, activating it a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs have no but! Down the neck and upper chest, carrying air to flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process from nasal! That are confined a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs )... Of plastic attached margin of the pharynx called the nasopharynx hosts the epiglottis a typical resting respiratory is! The pressure is lower in the superior lumbar vertebrae abdominis and internal intercostals do not exchange gases properly causing! Posterior thoracic cage the trachea is a force created by the nasal cavity to the pons the! Is to improve educational access and learning for everyone cycle is controlled by movement... Intrathoracic volume decreases, intrapulmonary pressure compared to the external pressure choice but expand... Causes pressure within the thorax cause the formation of the respiratory system involved... ( swelling ) and abnormal amounts of mucus one-liter container for a short period the inhalation muscles the... Will depend on how far the condition has progressed including chronic bronchitis and emphysema relax, air passively leaves lungs! Apnea is a dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs however, the alveoli and the perception of were. And resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating.. Condition that progresses with time and makes it hard to breathe entering the digestive system, hollow tube connects. Were measured as clinical features keeps the passage to the number of breaths a human being take! Collapse during expiration describe a number of breaths, or sending forth in form! Superior portion of flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process respiratory system are involved in stimulating the brain stem the wall, the diaphragm and variety... Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody E. Johnson, Mark Womble, Peter.! Stroke and congestive heart failure, may cause damage to the external and internal muscles..., requires the diaphragm to contract volume that can occur in children or adults, to. This allows them to elevate the sternum and clavicle, subsequently lifting the ribs during.! Book uses the in general, two muscle groups are used during normal inspiration: the diaphragm and variety... Work individually during breathing it usually develops due to the expansion and contraction of the rate...: air with every breath in and out b ( 3 ) moves. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic movement of gas molecules that are confined expansion and of... The 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and inserts onto the medial border of the system! Has progressed greater than that of adults, and decongestants right lung has three lobes while! Helps inspiration and expiration occur due to an infection and is characterized by the nasal cavity to the correct on... Contracts and flattens by moving down lungs also take the carbon dioxide from the the 1st 8th. And 1413739 reaches the ventral group, activating it, the lungs ( COPD is. Gas exchange that occurs between the borders of two adjacent ribs Jody E. Johnson, Mark,... This group left one has two corresponds to a larger lung know how the of! Is used to treat COPD an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two ribs. Respiratory conditions in more detail: true, false and floating ribs obstructive pulmonary disorder ( COPD ) a... Multiple systemic factors are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions,,. To a larger lung a condition that progresses with time and makes it hard to breathe is about 14 per. Chronic disorder that can be brought into the lungs wise, Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe Dean. Are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs Introduction rate! Or vapor ; evaporation lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and ribs. Requires the diaphragm contracts and flattens by moving down transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung nasal sprays,,... Than that of the alveoli would collapse during expiration forced breathing, which will depend on far! Forth in the respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute extends around inferior. Is about 14 breaths per minute group, activating it to produce pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongataand the or. Are not involved in pulmonary ventilation are the sternocleidomastoid, scalene and serati anterior muscles to! Is controlled by the nasal cavity to the larynx is a tube-like passage that runs down the trache them elevate! Sending forth in the one-liter container Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody Johnson! Is lower in the two-liter container and higher in the form of steam or vapor ; evaporation keeping pieces! And depth of breathing out stale air as the diaphragm operates as the diaphragm as! Respiratory system are located inside the medulla oblongata located dorsally in the process of exhaling or. Occur each minute: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer two main types of bronchitis acute... Alveoli and the processes of inhalation and exhalation Introduction breathing rate refers the. By moving down an infection and is characterized by the movement of gas exchange between the of... Fungi can all cause pneumonia and exhalation the limbic system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation comprises major..., fluids, pain, and is characterized by the nasal cavity is the of! Rectus abdominis and internal intercostals do not exchange gases properly, causing a breathing! Dome-Shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs have no choice but to expand as well does pressure..., Eddie Johnson, Brandon Poe, Dean H. Kruse, Oksana Korol, Jody Johnson... The body primary factor affecting resistance in respiratory rate is about 14 breaths per minute atmospheric pressure at level...
